What is RAG? A Practical Guide to Retrieval-Augmented Generation

Large Language Models (LLMs) such as GPT have changed how we interact with software. They can write, summarize, reason, and converse in ways that feel remarkably human. However, despite their capabilities, these models have an important limitation.
They do not actually “know” your data.
An LLM’s knowledge is frozen at the time it was trained. It has no awareness of your internal documents, your company policies, your latest product updates, or the private information stored in your systems. When asked questions outside of its training data, the model may guess. Sometimes confidently and incorrectly.
This limitation is why Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) exists.
What is RAG?
Retrieval-Augmented Generation, commonly referred to as RAG, is a technique that enhances an LLM’s responses by grounding them in external data. Instead of relying solely on what the model learned during training, RAG allows the system to retrieve relevant information from a separate knowledge source and provide it to the model at the moment it generates an answer.
In simple terms, RAG teaches an AI system to look things up before responding.
When a user asks a question, the system first searches a curated knowledge base for relevant content. Only after this retrieval step does the language model generate a response, using the retrieved information as context. This dramatically improves accuracy, relevance, and trustworthiness.
How RAG Works (Step by Step)
At a high level, RAG has two phases: retrieval and generation.
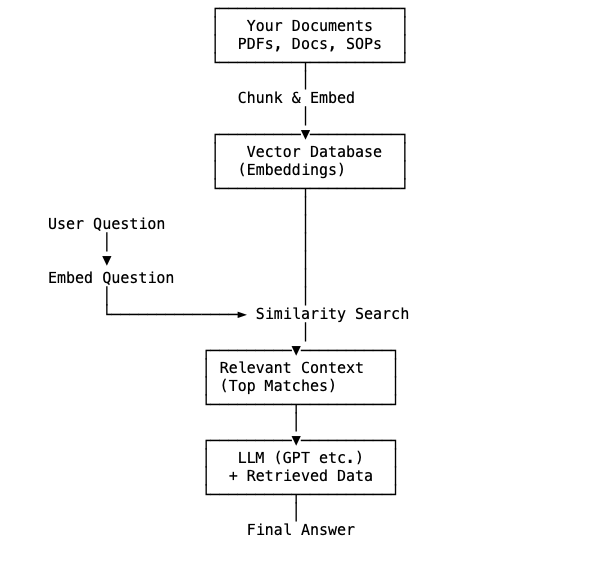
Step 1: Index Your Data
Your documents are:
- Split into chunks
- Converted into embeddings (vector representations)
- Stored in a vector database
Examples of data:
- PDFs
- Notion pages
- Help center articles
- Contracts
- CRM records
Step 2: Retrieve Relevant Context
When a user asks a question:
- The question is converted into an embedding
- The system searches for the most relevant chunks
- Only the best matches are selected
Step 3: Generate an Answer
The retrieved content is:
- Injected into the prompt as context
- Sent to the LLM
- Used to produce a fact-grounded response
The model doesn’t guess since it answers based on retrieved facts.
RAG vs Fine-Tuning
You may ask, why not fine-tune the model instead?
While fine-tuning and RAG are often mentioned together, they solve very different problems. Fine-tuning changes how a model behaves. It is useful for adjusting tone, response style, or output format, such as making answers more concise or enforcing a fixed structure. However, fine-tuning is not designed for managing knowledge. It does not reliably teach the model new or changing facts, and updating it requires retraining the model again.
RAG takes a more practical approach. Instead of embedding information inside the model, it allows the model to retrieve the right data at the time a question is asked. This makes it easy to keep answers accurate and up to date without touching the model itself.
In real world systems where policies, documents, and data change frequently, RAG is safer, faster, and far more scalable than repeatedly fine-tuning a model.
Real-World Use Cases for RAG
One of the most common applications of RAG is customer support. Instead of relying on generic responses, a RAG-powered assistant can retrieve the correct policy, invoice data, or troubleshooting guide and provide a precise, context-aware answer.
RAG is also widely used for internal knowledge assistants. Employees can ask natural-language questions such as “How do I request production access?” and receive answers sourced directly from internal documentation.
In sales and pre-sales scenarios, RAG ensures that AI assistants always reference the latest pricing, features, and terms, reducing the risk of misinformation.
Across all of these use cases, the value of RAG lies in its ability to deliver accurate answers without requiring users to manually search through documents.
RAG as the Foundation for Agentic AI
RAG is often the first step toward more agentic AI systems. While RAG enables accurate question answering, agents build on top of RAG to perform actions.
In an agentic system, one agent may retrieve relevant knowledge, another may validate it against company policies, and another may execute a task such as updating a CRM record or scheduling an appointment. In this context, RAG becomes the knowledge layer that powers intelligent decision-making.
In Knoon, RAG is built directly into the platform and works automatically in the background. Every agent can connect to your documents, help articles, internal guides, spreadsheets, and other knowledge sources. When someone asks a question, Knoon first finds the most relevant information from your knowledge base and then uses it to generate the answer. This means the response is based on real and up to date information, not guesses. You do not need to fine tune models or write complex prompts. Because RAG is part of Knoon’s core design, agents always use the right knowledge before they reply or take action.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation represents a shift from purely generative AI to grounded, reliable systems that can operate in real business environments. It bridges the gap between powerful language models and the structured, private data that organizations rely on every day.
If you want AI that is accurate, trustworthy, and genuinely useful, RAG is not just a feature.
It is a foundational capability.

